De-risk assessment: ANIMATED: An Intelligent Machine-to-Machine Framework for Services Based on Satellite Planetary and Earth Observation and Exploration Data
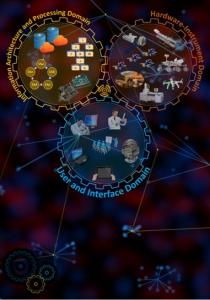
Objective(s): The objective is to develop a new framework that is based on the concept of Machine-to-Machine communications and automation, and of a new meta-language, with which data, methods, and standards are integrated in the form of dynamic ontologies and intelligent agents. The second should handle all operations and processing of the data, wherever these are stored, leading to automated interpretations which can be used both by humans and machines. This information should be communicated between them, also guiding each other during research and exploration activities. Our practical objective was also to design and test in the field a scenario that involves a set of instruments, appropriate for geological and astrobiological field work. Such a framework has numerous commercial applications, since it is designed to be a superset of the ‘Internet-of-Things’ concept. Especially in this project, the way instruments output their data should be affected, how these results are used to publish scientific knowledge.
Background and justification: Machine-to-Machine (M2M) automation is a powerful concept that will be used for large missions, many scientific and technological applications, as well as commercial activities on Earth. To achieve this, a smart communication network and clever protocols are required for every hardware or software entity that is part of the system. When focusing on autonomous Earth and Space exploration, it is required to define protocols and standards to dynamically handle scientific data output formats and methods during analysis and characterisation. For this purpose, we find necessary the development off a new architecture which is based on a new meta-language that merges data, protocols, and methods under a single structure. Interpretation should be therefore automated through intelligent agents acting on every form of memory or data storage (i.e., big cloud databases, local memory on devices). All acquired information should be converted into dense knowledge structures. We also intent to affect the way we review science, handle intellectual rights, and publish data. This is compulsory today because redundancy of information that come from a plurality of opinions and publishing means is a need. Dense knowledge structures should be formed which can be used equally by instruments and systems of instruments, as well as by humans, in a secure way.
Achievements and status: We have reviewed the major technologies on the machine-to-machine concept and have selected existing language platforms that can be integrated into a new meta-language, which can effectively merge all types of data and formats, methods, standards, communications, and decision-making algorithms under a universal informational structure. We have provided some examples on how these can be integrated and be used. We have also designed a setup of representative set of instruments that can use the new framework to perform automated field work on selected geological areas which are terrestrial analogues for planetary and astrobiological research. This plan involves humans as well. We have already selected commercial instruments and devices that can be easily adapted by us and have identified all the parts that require modification. We gave also examples on how current meta-data and data-structures can be translated to the new meta-language, and how instrument output can be re-written and standardized with this, as well as be secure.
Benefits: Integrating data and methods into intelligent software pieces that can talk the same language is a powerful way to automate missions. Instruments can then work unattended with a swarm intelligence. This has also huge potential for space missions and for commercial applications because many activities can be automated. ESA can benefit from this because it will be able to describe existing data into this new format and provide direct access to these data to instruments in order to automate many processes. The same can be applied in all aspects where machines need to take decisions, information must be continuously re-evaluated, credits should be properly handled, and data be secured.
