Model Based Cybernetics Software for the control of complex systems
Programme
TDE
Programme Reference
T722-602MM
Prime Contractor
UCA/UNIVERSITE CLERMONT AUVERGNE
Subcontractors
ENGINSOFT SPA
Italy
SHERPA ENGINEERING
France
Start Date
End Date
Status
Closed
Country
France
Objectives
To develop model based cybernetics software tools to improve the control of complex systems
Description
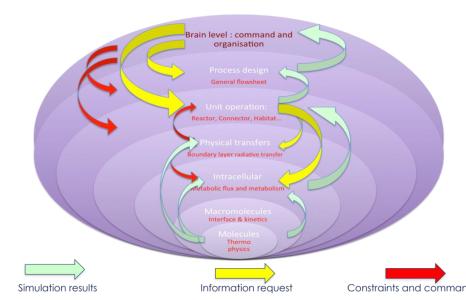
Future advanced life support systems relying on biochemical processes and GNC systems are known to be complex to model, due to their nonlinearity, high dynamic range of their response. Susceptibility to drifts in these systems (self adaptation, bias?) can be a threat (in case of GNC, loss of accuracy, which, even if small in increments, can lead to catastrophic misalignments e.g. for interplanetary missions) or present as well an interesting robustness to internal or external influences for biochemical systems, which may react and adapt to these stressors.
Robust resilience and stability (and proper desired system behavior) requires careful use of feedback control.
This involves all levels of system organization, a control loop or, e.g. for a biochemical system all levels from the genetic, metabolic to the cellular level and the process conditions (e.g. flow, pH, temperature, nutrients).
Recently, major progresses have been done in characterization of complex networks, but they rarely include random stressors. For instance, the understanding of radiation effects on biological systems are generally based on meta-data analysis which are by nature poorly compatible with the limited statistics and uniqueness of space exploration.
This activity shall provide an overview of challenging Biochemical systems and complex GNC systems for space applications and subsystems, that need special attention in future ESA missions.
Model based Cybernetics Software Tools using advanced control concepts (e.g. complex system modelling, predictive, and self-adapting control tools) shall be developed for this purpose.
Academic benchmark cases (e.g. MELiSSA thermophilic microbial waste degradation, complex GNC cases) shall be developed to investigate and demonstrate the benefits of formal model based control approaches for the management of complex systems.
Predicted results from the model based tools shall be assessed with experimental results. Recommendations for future research and technology directions in modeling, simulation and control to complex systems shall be provided.
Application Domain
Generic Technologies
Technology Domain
22 - Environmental Control & Life Support (ECLS) and In Situ Resource Utilisation (ISRU)
Competence Domain
6-Life & Physical Science Payloads, Life Support, Robotics & Automation
Initial TRL
TRL 2
Target TRL
TRL 3
Public Document
Executive Summary
