ROBOFAB: Robotic Fabrication for Space Applications
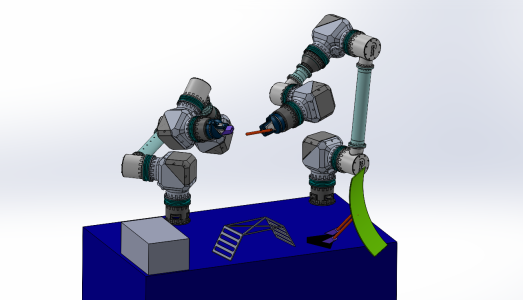
In-Space Assembly and Manufacturing (ISAM) is a revolutionary approach to building and maintaining space infrastructure. By constructing and fabricating components directly in orbit or beyond, ISAM reduces the reliance on Earth-based manufacturing and launch constraints, offering numerous advantages for space exploration, commercial applications, and sustainability. ROBOFAB was proposed as a mission study for redefining how large and complex structures are manufactured and assembled in orbit. Traditional methods rely on launching pre-fabricated components, which require costly, complex, and failure-prone folding mechanisms to fit within rocket fairings.
ROBOFAB eliminates this constraint by enabling direct in-space fabrication, streamlining the assembly process, and expanding the architectural possibilities for large-scale structures. The ROBOFAB mission study analysed the on-demand fabrication of large-scale structures in space by utilizing advanced robotic arms, carbon tube manufacturing, and 3D printing. Unlike previous space robotic systems, ROBOFAB’s robotic arms incorporate torque control technology, offering superior sensitivity and adaptability for assembly and manufacturing tasks in microgravity. This approach enables precise manipulation of materials and the autonomous assembly of complex structures. The mission also introduces an innovative carbon tube manufacturing process, which forms cylindrical tubes from pre-cured flat sections of carbon fibre polymer. This technique significantly reduces launch volume and mass while providing durable structural components essential for space infrastructure. Additionally, ROBOFAB integrates advanced 3D printing systems optimized for microgravity, allowing the fabrication of intermediate components directly in space with minimal material waste. These printers leverage proven technologies like Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM), which has been successfully tested aboard the ISS. To enhance operational efficiency, the mission employs autonomous robotic systems, capable of executing intricate fabrication tasks with minimal human intervention. By integrating shared autonomy, ROBOFAB maximizes automation for routine tasks while allowing operators to address complex challenges when necessary.
